Using Turborepo with GitLab CI
The following example shows how to use Turborepo with GitLab CI (opens in a new tab).
For a given root package.json:
{
"name": "my-turborepo",
"scripts": {
"build": "turbo run build",
"test": "turbo run test"
},
"devDependencies": {
"turbo": "1.2.5"
}
}And a turbo.json:
{
"$schema": "https://turbo.build/schema.json",
"pipeline": {
"build": {
"outputs": [".svelte-kit/**"],
"dependsOn": ["^build"]
},
"test": {
"dependsOn": ["^build"]
},
}
}Create a file called .gitlab-ci.yml in your repository with the following contents:
image: node:latest
stages:
- build
build:
stage: build
script:
- npm install
- npm run build
- npm run testRemote Caching
To use Remote Caching with GitLab CI, add the following environment variables to your GitLab CI project.
TURBO_TOKEN- The Bearer token to access the Remote CacheTURBO_TEAM- The account to which the monorepo belongs
To use Vercel Remote Caching, you can get the value of these variables in a few steps:
- Create a Scoped Access Token to your account in the Vercel Dashboard (opens in a new tab)
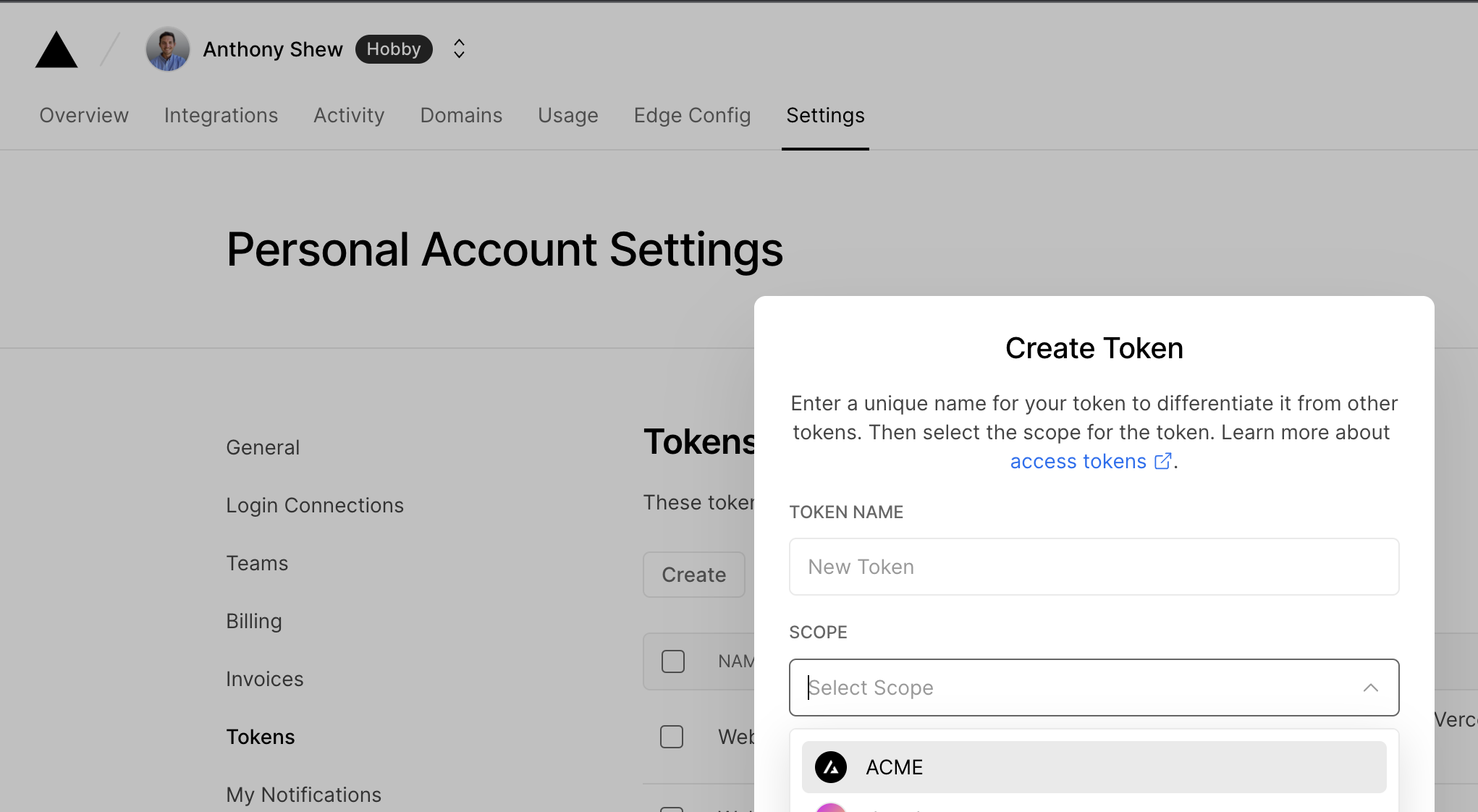
Copy the value to a safe place. You'll need it in a moment.
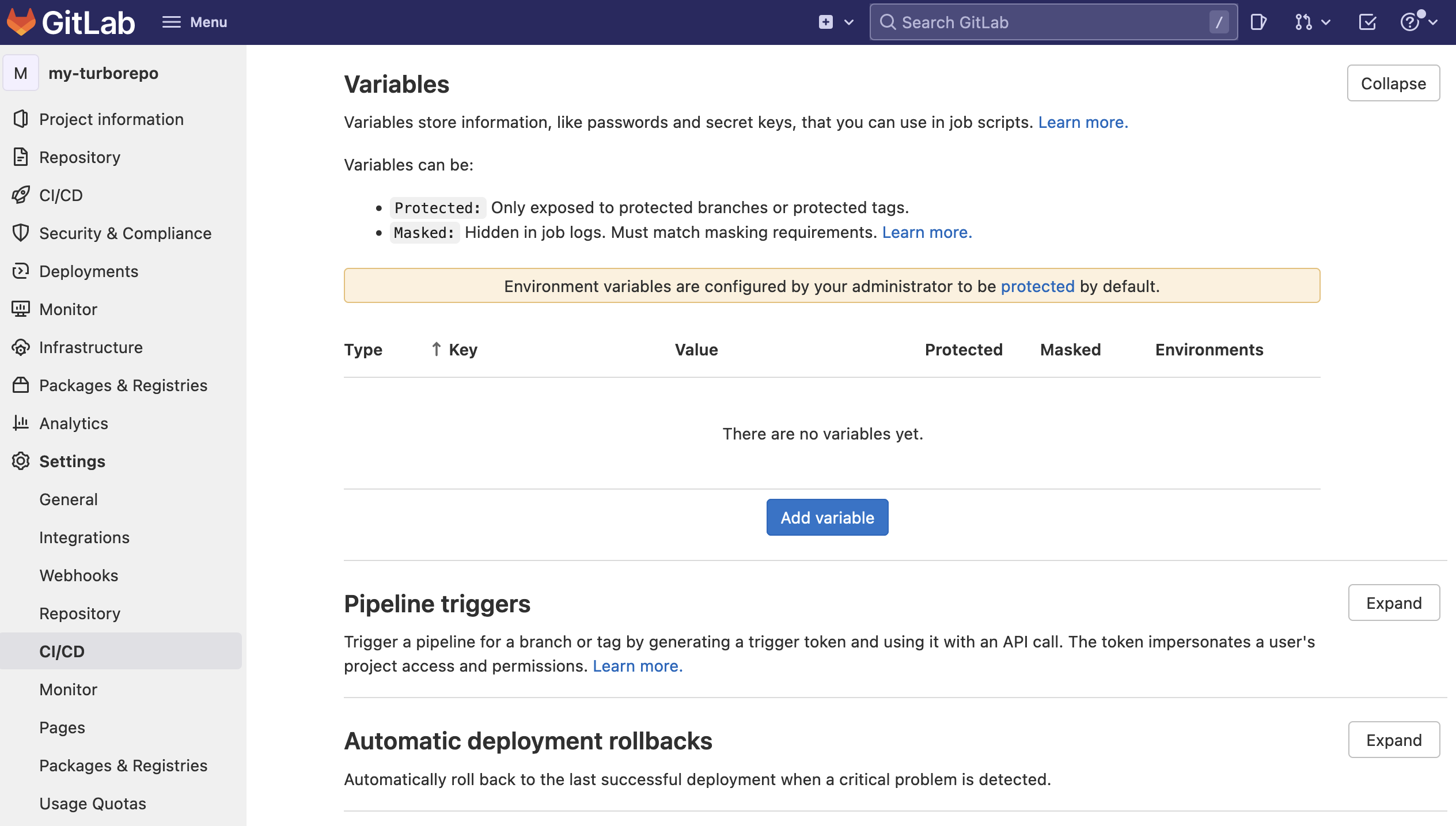
- Go to your GitLab repository settings and click on the Settings and then CI/CD tab. Create a new variable called
TURBO_TOKENand enter the value of your Scoped Access Token.
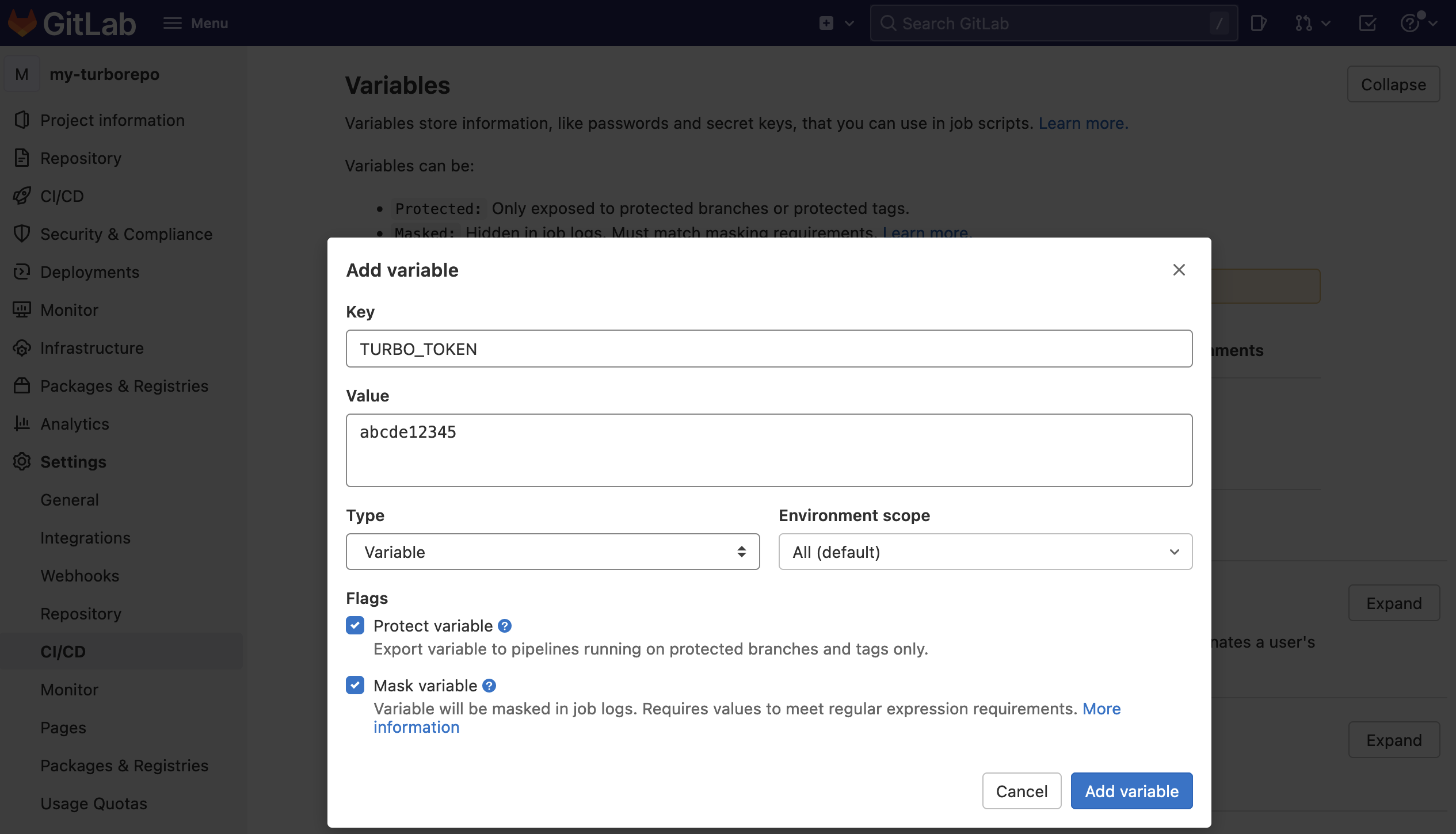
-
Make a second secret called
TURBO_TEAMand enter the value of your team's Vercel URL without thevercel.com/. Your Team URL can be found inside your team's general project settings from the dashboard.If you're using a Hobby Plan, you can use your username. Your username can be found in your Vercel Personal Account Settings (opens in a new tab)
